pgr_isPlanar - Experimental - pgRouting Manual (3.2)

pgr_isPlanar - Experimental
pgr_isPlanar
- Returns a boolean depending upon the planarity of the graph.

Warning
Possible server crash
-
These functions might create a server crash
Warning
Experimental functions
-
They are not officially of the current release.
-
They likely will not be officially be part of the next release:
-
The functions might not make use of ANY-INTEGER and ANY-NUMERICAL
-
Name might change.
-
Signature might change.
-
Functionality might change.
-
pgTap tests might be missing.
-
Might need c/c++ coding.
-
May lack documentation.
-
Documentation if any might need to be rewritten.
-
Documentation examples might need to be automatically generated.
-
Might need a lot of feedback from the comunity.
-
Might depend on a proposed function of pgRouting
-
Might depend on a deprecated function of pgRouting
-
Availability
-
Version 3.2.0
-
New experimental function
-
Description
A graph is planar if it can be drawn in two-dimensional space with no two of its edges crossing. Such a drawing of a planar graph is called a plane drawing. Every planar graph also admits a straight-line drawing, which is a plane drawing where each edge is represented by a line segment. When a graph has \(K_5\) or \(K_{3,3}\) as subgraph then the graph is not planar.
- The main characteristics are:
-
-
This implementation use the Boyer-Myrvold Planarity Testing.
-
It will return a boolean value depending upon the planarity of the graph.
-
Applicable only for undirected graphs.
-
The algorithm does not considers traversal costs in the calculations.
-
Running time: \(O(V)\)
-
Signatures
Summary
pgr_isPlanar(Edges SQL) -- Experimental on v3.2
RETURNS BOOLEAN
SELECT * FROM pgr_isPlanar(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost
FROM edge_table'
);
pgr_isplanar
--------------
t
(1 row)
Parameters
|
Parameter |
Type |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Edges SQL |
|
SQL query as described below. |
Inner query
- Edges SQL :
-
an SQL query, which should return a set of rows with the following columns:
|
Column |
Type |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
id |
|
Identifier of the edge. |
|
|
source |
|
Identifier of the first end point vertex of the edge. |
|
|
target |
|
Identifier of the second end point vertex of the edge. |
|
|
cost |
|
|
|
|
reverse_cost |
|
-1 |
|
Where:
- ANY-INTEGER :
-
SMALLINT, INTEGER, BIGINT
- ANY-NUMERICAL :
-
SMALLINT, INTEGER, BIGINT, REAL, FLOAT
Result Columns
Returns a boolean
(pgr_isplanar)
|
Column |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
pgr_isplanar |
|
|
Additional Example:
The following edges will make the subgraph with vertices {3, 4, 6, 9, 16} a \(K_5\) graph.
INSERT INTO edge_table (source, target, cost, reverse_cost) VALUES
(3, 9, 1, 1), (3, 16, 1, 1),
(4, 6, 1, 1), (4, 16, 1, 1),
(6, 16, 1, 1),
(9, 16, 1, 1);
INSERT 0 6
The new graph is not planar because it has a \(K_5\) subgraph. Edges in blue represent \(K_5\) subgraph.
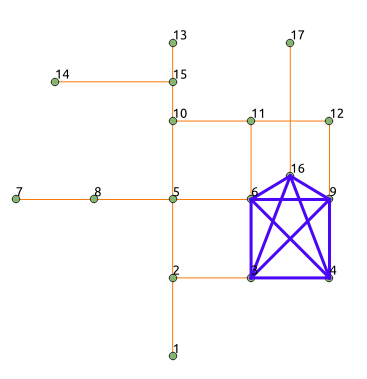
SELECT * FROM pgr_isPlanar(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost
FROM edge_table'
);
pgr_isplanar
--------------
f
(1 row)
See Also
-
The queries use the Sample Data network.
Indices and tables