Sample Data - pgRouting Manual (3.8)
Sample Data
The documentation provides very simple example queries based on a small sample network that resembles a city. To be able to execute the majority of the examples queries, follow the instructions below.
Main graph
A graph consists of a set of edges and a set of vertices.
The following city is to be inserted into the database:
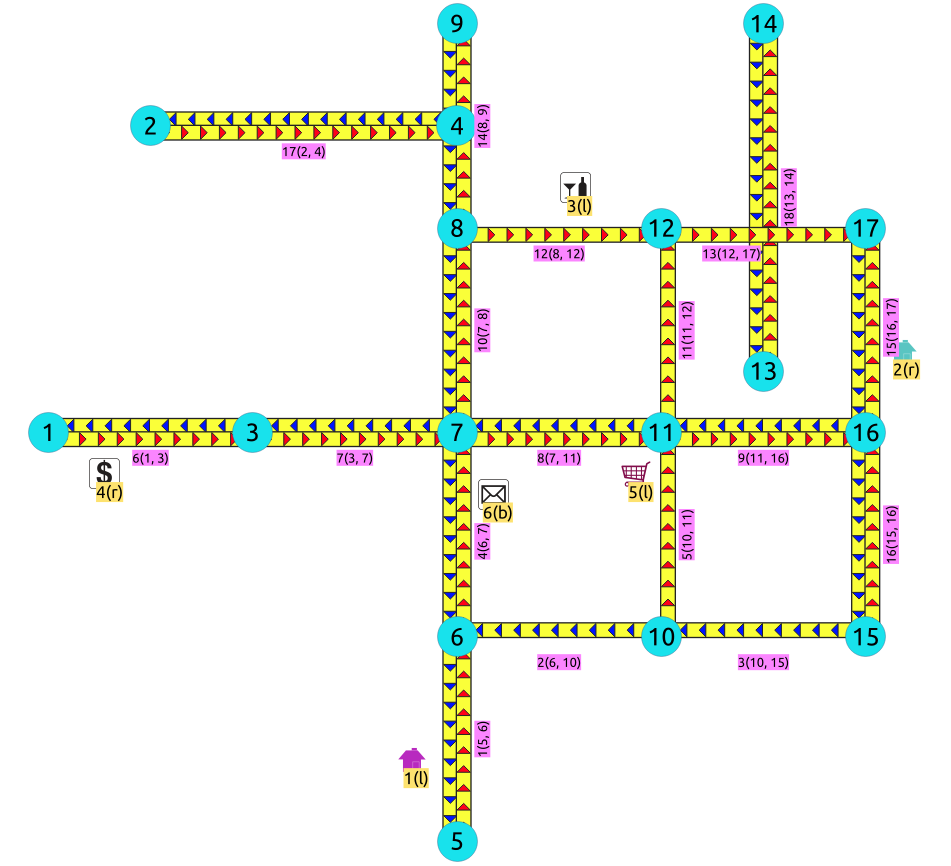
Information known at this point is the geometry of the edges, cost values, capacity values, category values and some locations that are not in the graph.
The process to have working topology starts by inserting the edges. After that everything else is calculated.
Edges
The database design for the documentation of pgRouting, keeps in the same row 2
segments, one in the direction of the geometry and the second in the opposite
direction. Therefore some information has the
reverse_
prefix which
corresponds to the segment on the opposite direction of the geometry.
|
Column |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
A unique identifier. |
|
|
Identifier of the starting vertex of the geometry
|
|
|
Identifier of the ending vertex of the geometry
|
|
|
Cost to traverse from
source
to
|
|
|
Cost to traverse from
target
to
|
|
|
Flow capacity from
source
to
|
|
|
Flow capacity from
target
to
|
|
|
Flow capacity from
target
to
|
|
|
Flow capacity from
target
to
|
|
|
\(x\) coordinate of the starting vertex of the geometry.
|
|
|
\(y\) coordinate of the ending vertex of the geometry.
|
|
|
The geometry of the segments. |
CREATE TABLE edges (
id BIGSERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
source BIGINT,
target BIGINT,
cost FLOAT,
reverse_cost FLOAT,
capacity BIGINT,
reverse_capacity BIGINT,
x1 FLOAT,
y1 FLOAT,
x2 FLOAT,
y2 FLOAT,
geom geometry
);
CREATE TABLE
Starting on PostgreSQL 12:
...
x1 FLOAT GENERATED ALWAYS AS (ST_X(ST_StartPoint(geom))) STORED,
y1 FLOAT GENERATED ALWAYS AS (ST_Y(ST_StartPoint(geom))) STORED,
x1 FLOAT GENERATED ALWAYS AS (ST_X(ST_EndPoint(geom))) STORED,
y1 FLOAT GENERATED ALWAYS AS (ST_Y(ST_EndPoint(geom))) STORED,
...
Optionally indexes on different columns can be created. The recommendation is to have
-
idindexed. -
sourceandtargetcolumns indexed to speed up pgRouting queries. -
geomindexed to speed up geometry processes that might be needed in the front end.
For this small example the indexes are skipped, except for
id
Edges data
Inserting into the database the information of the edges:
INSERT INTO edges (
cost, reverse_cost,
capacity, reverse_capacity, geom) VALUES
( 1, 1, 80, 130, ST_MakeLine(ST_POINT(2, 0), ST_POINT(2, 1))),
(-1, 1, -1, 100, ST_MakeLine(ST_POINT(2, 1), ST_POINT(3, 1))),
(-1, 1, -1, 130, ST_MakeLine(ST_POINT(3, 1), ST_POINT(4, 1))),
( 1, 1, 100, 50, ST_MakeLine(ST_POINT(2, 1), ST_POINT(2, 2))),
( 1, -1, 130, -1, ST_MakeLine(ST_POINT(3, 1), ST_POINT(3, 2))),
( 1, 1, 50, 100, ST_MakeLine(ST_POINT(0, 2), ST_POINT(1, 2))),
( 1, 1, 50, 130, ST_MakeLine(ST_POINT(1, 2), ST_POINT(2, 2))),
( 1, 1, 100, 130, ST_MakeLine(ST_POINT(2, 2), ST_POINT(3, 2))),
( 1, 1, 130, 80, ST_MakeLine(ST_POINT(3, 2), ST_POINT(4, 2))),
( 1, 1, 130, 50, ST_MakeLine(ST_POINT(2, 2), ST_POINT(2, 3))),
( 1, -1, 130, -1, ST_MakeLine(ST_POINT(3, 2), ST_POINT(3, 3))),
( 1, -1, 100, -1, ST_MakeLine(ST_POINT(2, 3), ST_POINT(3, 3))),
( 1, -1, 100, -1, ST_MakeLine(ST_POINT(3, 3), ST_POINT(4, 3))),
( 1, 1, 80, 130, ST_MakeLine(ST_POINT(2, 3), ST_POINT(2, 4))),
( 1, 1, 80, 50, ST_MakeLine(ST_POINT(4, 2), ST_POINT(4, 3))),
( 1, 1, 80, 80, ST_MakeLine(ST_POINT(4, 1), ST_POINT(4, 2))),
( 1, 1, 130, 100, ST_MakeLine(ST_POINT(0.5, 3.5), ST_POINT(1.999999999999, 3.5))),
( 1, 1, 50, 130, ST_MakeLine(ST_POINT(3.5, 2.3), ST_POINT(3.5, 4)));
INSERT 0 18
Negative values on the cost, capacity and category means that the edge do not exist.
Vertices
The vertex information is calculated based on the identifier of the edge and the geometry and saved on a table. Saving all the information provided by pgr_extractVertices :
SELECT * INTO vertices
FROM pgr_extractVertices('SELECT id, geom FROM edges ORDER BY id');
SELECT 17
In this case the because the
CREATE
statement was not used, the definition
of an index on the table is needed.
CREATE SEQUENCE vertices_id_seq;
CREATE SEQUENCE
ALTER TABLE vertices ALTER COLUMN id SET DEFAULT nextval('vertices_id_seq');
ALTER TABLE
ALTER SEQUENCE vertices_id_seq OWNED BY vertices.id;
ALTER SEQUENCE
SELECT setval('vertices_id_seq', (SELECT coalesce(max(id)) FROM vertices));
setval
--------
17
(1 row)
The structure of the table is:
Table "public.vertices"
Column Type Collation Nullable Default
-----------+------------------+-----------+----------+--------------------------------------
id bigint nextval('vertices_id_seq'::regclass)
in_edges bigint[]
out_edges bigint[]
x double precision
y double precision
geom geometry
Vertices data
The saved information of the vertices is:
SELECT * FROM vertices;
id in_edges out_edges x y geom
----+----------+-----------+----------------+-----+--------------------------------------------
1 {6} 0 2 010100000000000000000000000000000000000040
2 {17} 0.5 3.5 0101000000000000000000E03F0000000000000C40
3 {6} {7} 1 2 0101000000000000000000F03F0000000000000040
4 {17} 1.999999999999 3.5 010100000068EEFFFFFFFFFF3F0000000000000C40
5 {1} 2 0 010100000000000000000000400000000000000000
6 {1} {2,4} 2 1 01010000000000000000000040000000000000F03F
7 {4,7} {8,10} 2 2 010100000000000000000000400000000000000040
8 {10} {12,14} 2 3 010100000000000000000000400000000000000840
9 {14} 2 4 010100000000000000000000400000000000001040
10 {2} {3,5} 3 1 01010000000000000000000840000000000000F03F
11 {5,8} {9,11} 3 2 010100000000000000000008400000000000000040
12 {11,12} {13} 3 3 010100000000000000000008400000000000000840
13 {18} 3.5 2.3 01010000000000000000000C406666666666660240
14 {18} 3.5 4 01010000000000000000000C400000000000001040
15 {3} {16} 4 1 01010000000000000000001040000000000000F03F
16 {9,16} {15} 4 2 010100000000000000000010400000000000000040
17 {13,15} 4 3 010100000000000000000010400000000000000840
(17 rows)
Here is where adding more columns to the vertices table can be done. Additional columns names and types will depend on the application.
The topology
This queries based on the vertices data create a topology by filling the
source
and
target
columns in the edges table.
/* -- set the source information */
UPDATE edges AS e
SET source = v.id, x1 = x, y1 = y
FROM vertices AS v
WHERE ST_StartPoint(e.geom) = v.geom;
UPDATE 18
/* -- set the target information */
UPDATE edges AS e
SET target = v.id, x2 = x, y2 = y
FROM vertices AS v
WHERE ST_EndPoint(e.geom) = v.geom;
UPDATE 18
Topology data
SELECT id, source, target
FROM edges ORDER BY id;
id source target
----+--------+--------
1 5 6
2 6 10
3 10 15
4 6 7
5 10 11
6 1 3
7 3 7
8 7 11
9 11 16
10 7 8
11 11 12
12 8 12
13 12 17
14 8 9
15 16 17
16 15 16
17 2 4
18 13 14
(18 rows)
Points outside the graph
Points of interest
Some times the applications work "on the fly" starting from a location that is not a vertex in the graph. Those locations, in pgRrouting are called points of interest.
The information needed in the points of interest is
pid
,
edge_id
,
side
,
fraction
.
On this documentation there will be some 6 fixed points of interest and they will be stored on a table.
|
Column |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
A unique identifier. |
|
|
Identifier of the nearest segment. |
|
|
Is it on the left, right or both sides of the segment
|
|
|
Where in the segment is the point located. |
|
|
The geometry of the points. |
|
|
The distance between
|
|
|
A segment that connects the
|
|
|
A point on segment
|
CREATE TABLE pointsOfInterest(
pid BIGSERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
edge_id BIGINT,
side CHAR,
fraction FLOAT,
distance FLOAT,
edge geometry,
newPoint geometry,
geom geometry);
IF v > 3.4 THEN
Points of interest fill up
Inserting the points of interest.
INSERT INTO pointsOfInterest (geom) VALUES
(ST_Point(1.8, 0.4)),
(ST_Point(4.2, 2.4)),
(ST_Point(2.6, 3.2)),
(ST_Point(0.3, 1.8)),
(ST_Point(2.9, 1.8)),
(ST_Point(2.2, 1.7));
Filling the rest of the table.
UPDATE pointsofinterest SET
edge_id = poi.edge_id,
side = poi.side,
fraction = round(poi.fraction::numeric, 2),
distance = round(poi.distance::numeric, 2),
edge = poi.edge,
newPoint = ST_EndPoint(poi.edge)
FROM (
SELECT *
FROM pgr_findCloseEdges(
$$SELECT id, geom FROM edges$$,(SELECT array_agg(geom) FROM pointsOfInterest), 0.5) ) AS poi
WHERE pointsOfInterest.geom = poi.geom;
Any other additional modification: In this manual, point \(6\) can be reached from both sides.
UPDATE pointsOfInterest SET side = 'b' WHERE pid = 6;
The points of interest:
SELECT
pid, ST_AsText(geom) geom,
edge_id, fraction AS frac, side, distance AS dist,
ST_AsText(edge) edge, ST_AsText(newPoint) newPoint
FROM pointsOfInterest;
pid geom edge_id frac side dist edge newpoint
-----+----------------+---------+------+------+------+---------------------------+--------------
1 POINT(1.8 0.4) 1 0.4 l 0.2 LINESTRING(1.8 0.4,2 0.4) POINT(2 0.4)
4 POINT(0.3 1.8) 6 0.3 r 0.2 LINESTRING(0.3 1.8,0.3 2) POINT(0.3 2)
3 POINT(2.6 3.2) 12 0.6 l 0.2 LINESTRING(2.6 3.2,2.6 3) POINT(2.6 3)
2 POINT(4.2 2.4) 15 0.4 r 0.2 LINESTRING(4.2 2.4,4 2.4) POINT(4 2.4)
5 POINT(2.9 1.8) 5 0.8 l 0.1 LINESTRING(2.9 1.8,3 1.8) POINT(3 1.8)
6 POINT(2.2 1.7) 4 0.7 b 0.2 LINESTRING(2.2 1.7,2 1.7) POINT(2 1.7)
(6 rows)
Support tables
Combinations
Many functions can be used with a combinations of
(source,
target)
pairs
when wanting a route from
source
to
target
.
For convenience of this documentation, some combinations will be stored on a table:
CREATE TABLE combinations (
source BIGINT,
target BIGINT
);
CREATE TABLE
Inserting the data:
INSERT INTO combinations (
source, target) VALUES
(5, 6),
(5, 10),
(6, 5),
(6, 15),
(6, 14);
INSERT 0 5
Combinations data
SELECT * FROM combinations;
source target
--------+--------
5 6
5 10
6 5
6 15
6 14
(5 rows)
Restrictions
Some functions accept soft restrictions about the segments.
The creation of the restrictions table
CREATE TABLE restrictions (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
path BIGINT[],
cost FLOAT
);
CREATE TABLE
Adding the restrictions
INSERT INTO restrictions (path, cost) VALUES
(ARRAY[4, 7], 100),
(ARRAY[8, 11], 100),
(ARRAY[7, 10], 100),
(ARRAY[3, 5, 9], 4),
(ARRAY[9, 16], 100);
INSERT 0 5
Restrictions data
SELECT * FROM restrictions;
id path cost
----+---------+------
1 {4,7} 100
2 {8,11} 100
3 {7,10} 100
4 {3,5,9} 4
5 {9,16} 100
(5 rows)
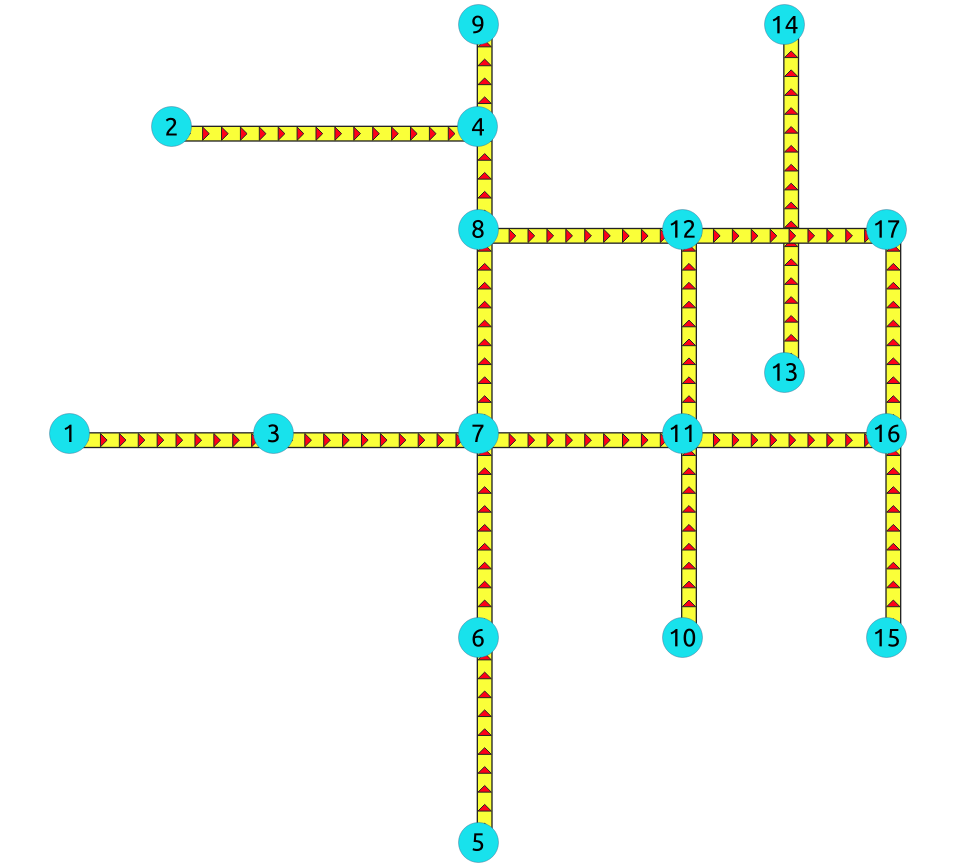
Images
-
Red arrows correspond when
cost> 0 in the edge table. -
Blue arrows correspond when
reverse_cost> 0 in the edge table. -
Points are outside the graph.
-
Click on the graph to enlarge.
Directed graph with
cost
and
reverse_cost
When working with city networks, this is recommended for point of view of vehicles.

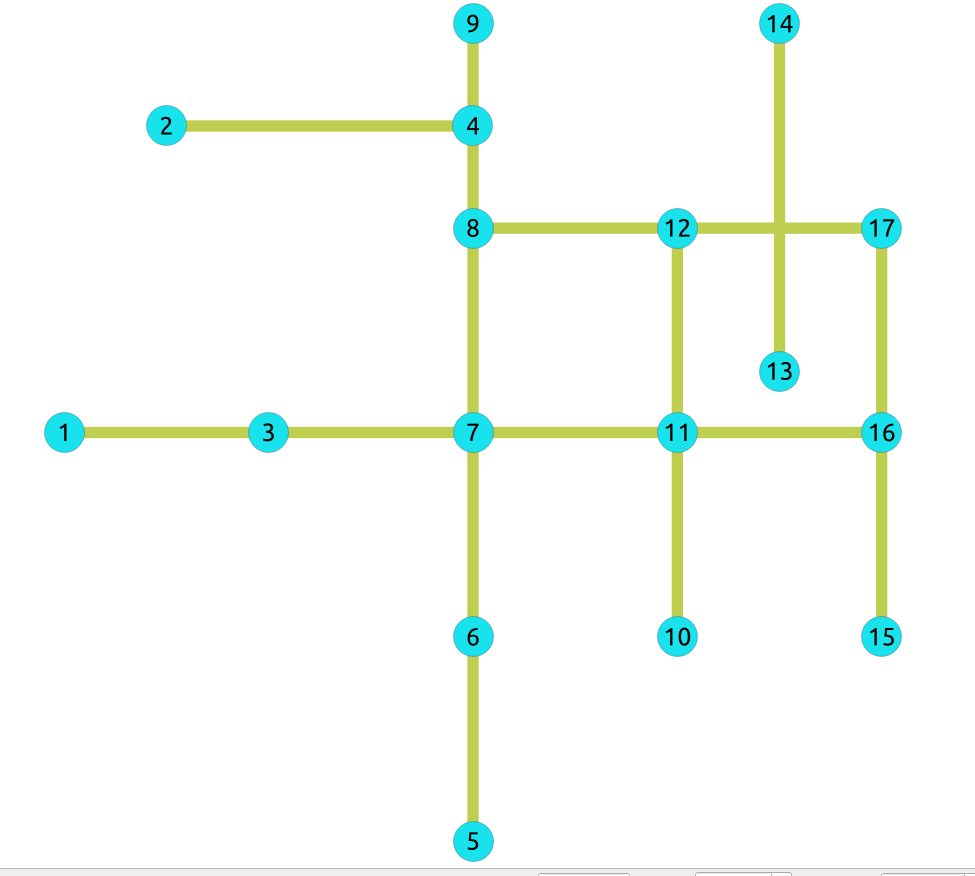
Undirected graph with
cost
and
reverse_cost
When working with city networks, this is recommended for point of view of pedestrians.
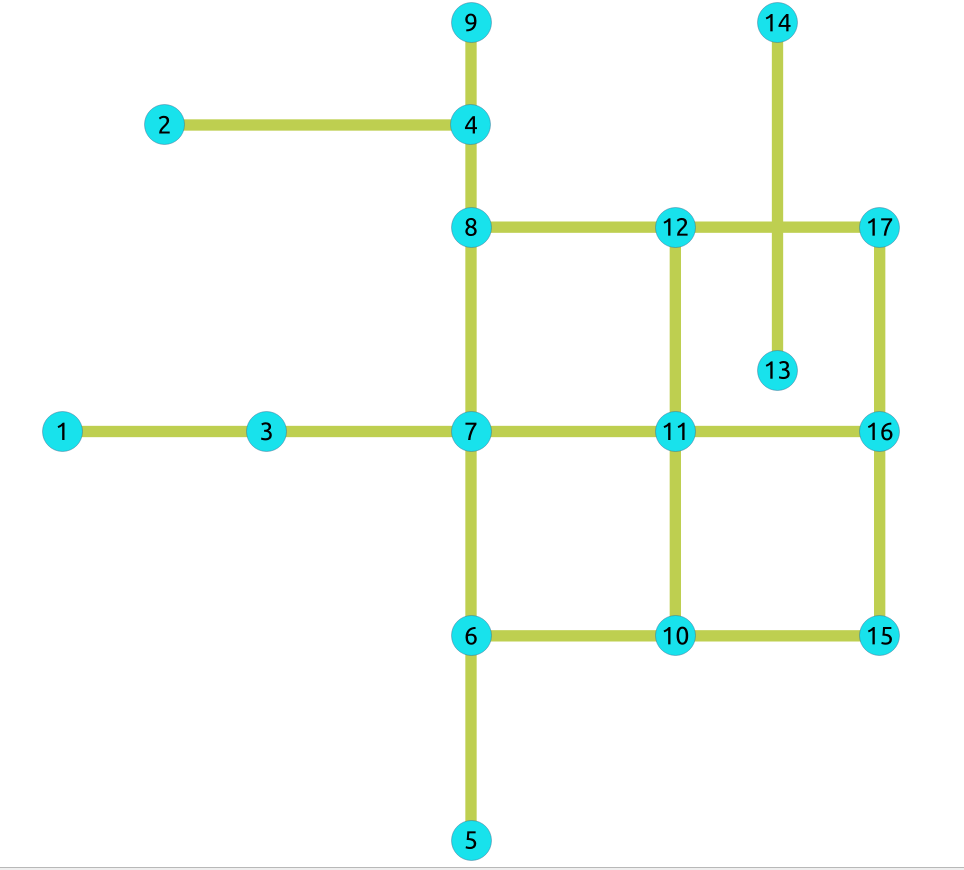
Directed graph with
cost
Undirected graph with
cost
Pick & Deliver Data
This data example lc101 is from data published at https://www.sintef.no/projectweb/top/pdptw/li-lim-benchmark/
The vehicles
There are 25 vehicles in the problem all with the same characteristics.
CREATE TABLE v_lc101(
id BIGINT NOT NULL primary key,
capacity BIGINT DEFAULT 200,
start_x FLOAT DEFAULT 30,
start_y FLOAT DEFAULT 50,
start_open INTEGER DEFAULT 0,
start_close INTEGER DEFAULT 1236);
CREATE TABLE
/* create 25 vehciles */
INSERT INTO v_lc101 (id)
(SELECT * FROM generate_series(1, 25));
INSERT 0 25
The original orders
The data comes in different rows for the pickup and the delivery of the same order.
CREATE table lc101_c(
id BIGINT not null primary key,
x DOUBLE PRECISION,
y DOUBLE PRECISION,
demand INTEGER,
open INTEGER,
close INTEGER,
service INTEGER,
pindex BIGINT,
dindex BIGINT
);
CREATE TABLE
/* the original data */
INSERT INTO lc101_c(
id, x, y, demand, open, close, service, pindex, dindex) VALUES
( 1, 45, 68, -10, 912, 967, 90, 11, 0),
( 2, 45, 70, -20, 825, 870, 90, 6, 0),
( 3, 42, 66, 10, 65, 146, 90, 0, 75),
( 4, 42, 68, -10, 727, 782, 90, 9, 0),
( 5, 42, 65, 10, 15, 67, 90, 0, 7),
( 6, 40, 69, 20, 621, 702, 90, 0, 2),
( 7, 40, 66, -10, 170, 225, 90, 5, 0),
( 8, 38, 68, 20, 255, 324, 90, 0, 10),
( 9, 38, 70, 10, 534, 605, 90, 0, 4),
( 10, 35, 66, -20, 357, 410, 90, 8, 0),
( 11, 35, 69, 10, 448, 505, 90, 0, 1),
( 12, 25, 85, -20, 652, 721, 90, 18, 0),
( 13, 22, 75, 30, 30, 92, 90, 0, 17),
( 14, 22, 85, -40, 567, 620, 90, 16, 0),
( 15, 20, 80, -10, 384, 429, 90, 19, 0),
( 16, 20, 85, 40, 475, 528, 90, 0, 14),
( 17, 18, 75, -30, 99, 148, 90, 13, 0),
( 18, 15, 75, 20, 179, 254, 90, 0, 12),
( 19, 15, 80, 10, 278, 345, 90, 0, 15),
( 20, 30, 50, 10, 10, 73, 90, 0, 24),
( 21, 30, 52, -10, 914, 965, 90, 30, 0),
( 22, 28, 52, -20, 812, 883, 90, 28, 0),
( 23, 28, 55, 10, 732, 777, 0, 0, 103),
( 24, 25, 50, -10, 65, 144, 90, 20, 0),
( 25, 25, 52, 40, 169, 224, 90, 0, 27),
( 26, 25, 55, -10, 622, 701, 90, 29, 0),
( 27, 23, 52, -40, 261, 316, 90, 25, 0),
( 28, 23, 55, 20, 546, 593, 90, 0, 22),
( 29, 20, 50, 10, 358, 405, 90, 0, 26),
( 30, 20, 55, 10, 449, 504, 90, 0, 21),
( 31, 10, 35, -30, 200, 237, 90, 32, 0),
( 32, 10, 40, 30, 31, 100, 90, 0, 31),
( 33, 8, 40, 40, 87, 158, 90, 0, 37),
( 34, 8, 45, -30, 751, 816, 90, 38, 0),
( 35, 5, 35, 10, 283, 344, 90, 0, 39),
( 36, 5, 45, 10, 665, 716, 0, 0, 105),
( 37, 2, 40, -40, 383, 434, 90, 33, 0),
( 38, 0, 40, 30, 479, 522, 90, 0, 34),
( 39, 0, 45, -10, 567, 624, 90, 35, 0),
( 40, 35, 30, -20, 264, 321, 90, 42, 0),
( 41, 35, 32, -10, 166, 235, 90, 43, 0),
( 42, 33, 32, 20, 68, 149, 90, 0, 40),
( 43, 33, 35, 10, 16, 80, 90, 0, 41),
( 44, 32, 30, 10, 359, 412, 90, 0, 46),
( 45, 30, 30, 10, 541, 600, 90, 0, 48),
( 46, 30, 32, -10, 448, 509, 90, 44, 0),
( 47, 30, 35, -10, 1054, 1127, 90, 49, 0),
( 48, 28, 30, -10, 632, 693, 90, 45, 0),
( 49, 28, 35, 10, 1001, 1066, 90, 0, 47),
( 50, 26, 32, 10, 815, 880, 90, 0, 52),
( 51, 25, 30, 10, 725, 786, 0, 0, 101),
( 52, 25, 35, -10, 912, 969, 90, 50, 0),
( 53, 44, 5, 20, 286, 347, 90, 0, 58),
( 54, 42, 10, 40, 186, 257, 90, 0, 60),
( 55, 42, 15, -40, 95, 158, 90, 57, 0),
( 56, 40, 5, 30, 385, 436, 90, 0, 59),
( 57, 40, 15, 40, 35, 87, 90, 0, 55),
( 58, 38, 5, -20, 471, 534, 90, 53, 0),
( 59, 38, 15, -30, 651, 740, 90, 56, 0),
( 60, 35, 5, -40, 562, 629, 90, 54, 0),
( 61, 50, 30, -10, 531, 610, 90, 67, 0),
( 62, 50, 35, 20, 262, 317, 90, 0, 68),
( 63, 50, 40, 50, 171, 218, 90, 0, 74),
( 64, 48, 30, 10, 632, 693, 0, 0, 102),
( 65, 48, 40, 10, 76, 129, 90, 0, 72),
( 66, 47, 35, 10, 826, 875, 90, 0, 69),
( 67, 47, 40, 10, 12, 77, 90, 0, 61),
( 68, 45, 30, -20, 734, 777, 90, 62, 0),
( 69, 45, 35, -10, 916, 969, 90, 66, 0),
( 70, 95, 30, -30, 387, 456, 90, 81, 0),
( 71, 95, 35, 20, 293, 360, 90, 0, 77),
( 72, 53, 30, -10, 450, 505, 90, 65, 0),
( 73, 92, 30, -10, 478, 551, 90, 76, 0),
( 74, 53, 35, -50, 353, 412, 90, 63, 0),
( 75, 45, 65, -10, 997, 1068, 90, 3, 0),
( 76, 90, 35, 10, 203, 260, 90, 0, 73),
( 77, 88, 30, -20, 574, 643, 90, 71, 0),
( 78, 88, 35, 20, 109, 170, 0, 0, 104),
( 79, 87, 30, 10, 668, 731, 90, 0, 80),
( 80, 85, 25, -10, 769, 820, 90, 79, 0),
( 81, 85, 35, 30, 47, 124, 90, 0, 70),
( 82, 75, 55, 20, 369, 420, 90, 0, 85),
( 83, 72, 55, -20, 265, 338, 90, 87, 0),
( 84, 70, 58, 20, 458, 523, 90, 0, 89),
( 85, 68, 60, -20, 555, 612, 90, 82, 0),
( 86, 66, 55, 10, 173, 238, 90, 0, 91),
( 87, 65, 55, 20, 85, 144, 90, 0, 83),
( 88, 65, 60, -10, 645, 708, 90, 90, 0),
( 89, 63, 58, -20, 737, 802, 90, 84, 0),
( 90, 60, 55, 10, 20, 84, 90, 0, 88),
( 91, 60, 60, -10, 836, 889, 90, 86, 0),
( 92, 67, 85, 20, 368, 441, 90, 0, 93),
( 93, 65, 85, -20, 475, 518, 90, 92, 0),
( 94, 65, 82, -10, 285, 336, 90, 96, 0),
( 95, 62, 80, -20, 196, 239, 90, 98, 0),
( 96, 60, 80, 10, 95, 156, 90, 0, 94),
( 97, 60, 85, 30, 561, 622, 0, 0, 106),
( 98, 58, 75, 20, 30, 84, 90, 0, 95),
( 99, 55, 80, -20, 743, 820, 90, 100, 0),
( 100, 55, 85, 20, 647, 726, 90, 0, 99),
( 101, 25, 30, -10, 725, 786, 90, 51, 0),
( 102, 48, 30, -10, 632, 693, 90, 64, 0),
( 103, 28, 55, -10, 732, 777, 90, 23, 0),
( 104, 88, 35, -20, 109, 170, 90, 78, 0),
( 105, 5, 45, -10, 665, 716, 90, 36, 0),
( 106, 60, 85, -30, 561, 622, 90, 97, 0);
INSERT 0 106
The orders
The original data needs to be converted to an appropriate table:
WITH deliveries AS (SELECT * FROM lc101_c WHERE dindex = 0)
SELECT
row_number() over() AS id, p.demand,
p.id as p_node_id, p.x AS p_x, p.y AS p_y, p.open AS p_open, p.close as p_close, p.service as p_service,
d.id as d_node_id, d.x AS d_x, d.y AS d_y, d.open AS d_open, d.close as d_close, d.service as d_service
INTO c_lc101
FROM deliveries as d JOIN lc101_c as p ON (d.pindex = p.id);
SELECT 53
SELECT * FROM c_lc101 LIMIT 1;
id demand p_node_id p_x p_y p_open p_close p_service d_node_id d_x d_y d_open d_close d_service
----+--------+-----------+-----+-----+--------+---------+-----------+-----------+-----+-----+--------+---------+-----------
1 10 3 42 66 65 146 90 75 45 65 997 1068 90
(1 row)