ST_ColorMap
Name
ST_ColorMap — Creates a new raster of up to four 8BUI bands (grayscale, RGB, RGBA) from the source raster and a specified band. Band 1 is assumed if not specified.
Synopsis
raster
ST_ColorMap
(
raster
rast
, integer
nband=1
, text
colormap=grayscale
, text
method=INTERPOLATE
)
;
raster
ST_ColorMap
(
raster
rast
, text
colormap
, text
method=INTERPOLATE
)
;
Description
Apply a
colormap
to the band at
nband
of
rast
resulting a new raster comprised of up to four 8BUI bands. The number of 8BUI bands in the new raster is determined by the number of color components defined in
colormap
.
If
nband
is not specified, then band 1 is assumed.
colormap
can be a keyword of a pre-defined colormap or a set of lines defining the value and the color components.
Valid pre-defined
colormap
keyword:
-
grayscaleorgreyscalefor a one 8BUI band raster of shades of gray. -
pseudocolorfor a four 8BUI (RGBA) band raster with colors going from blue to green to red. -
firefor a four 8BUI (RGBA) band raster with colors going from black to red to pale yellow. -
blueredfor a four 8BUI (RGBA) band raster with colors going from blue to pale white to red.
Users can pass a set of entries (one per line) to
colormap
to specify custom colormaps. Each entry generally consists of five values: the pixel value and corresponding Red, Green, Blue, Alpha components (color components between 0 and 255). Percent values can be used instead of pixel values where 0% and 100% are the minimum and maximum values found in the raster band. Values can be separated with commas (','), tabs, colons (':') and/or spaces. The pixel value can be set to
nv
,
null
or
nodata
for the NODATA value. An example is provided below.
5 0 0 0 255 4 100:50 55 255 1 150,100 150 255 0% 255 255 255 255 nv 0 0 0 0
The syntax of
colormap
is similar to that of the color-relief mode of GDAL
gdaldem
.
Valid keywords for
method
:
-
INTERPOLATEto use linear interpolation to smoothly blend the colors between the given pixel values -
EXACTto strictly match only those pixels values found in the colormap. Pixels whose value does not match a colormap entry will be set to 0 0 0 0 (RGBA) -
NEARESTto use the colormap entry whose value is closest to the pixel value
![[Note]](images/note.png)
|
|
|
A great reference for colormaps is ColorBrewer . |
![[Warning]](images/warning.png)
|
|
|
The resulting bands of new raster will have no NODATA value set. Use ST_SetBandNoDataValue to set a NODATA value if one is needed. |
Availability: 2.1.0
Examples
This is a junk table to play with
-- setup test raster table --
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS funky_shapes;
CREATE TABLE funky_shapes(rast raster);
INSERT INTO funky_shapes(rast)
WITH ref AS (
SELECT ST_MakeEmptyRaster( 200, 200, 0, 200, 1, -1, 0, 0) AS rast
)
SELECT
ST_Union(rast)
FROM (
SELECT
ST_AsRaster(
ST_Rotate(
ST_Buffer(
ST_GeomFromText('LINESTRING(0 2,50 50,150 150,125 50)'),
i*2
),
pi() * i * 0.125, ST_Point(50,50)
),
ref.rast, '8BUI'::text, i * 5
) AS rast
FROM ref
CROSS JOIN generate_series(1, 10, 3) AS i
) AS shapes;
SELECT ST_NumBands(rast) As n_orig, ST_NumBands(ST_ColorMap(rast,1, 'greyscale')) As ngrey, ST_NumBands(ST_ColorMap(rast,1, 'pseudocolor')) As npseudo, ST_NumBands(ST_ColorMap(rast,1, 'fire')) As nfire, ST_NumBands(ST_ColorMap(rast,1, 'bluered')) As nbluered, ST_NumBands(ST_ColorMap(rast,1, ' 100% 255 0 0 80% 160 0 0 50% 130 0 0 30% 30 0 0 20% 60 0 0 0% 0 0 0 nv 255 255 255 ')) As nred FROM funky_shapes;
n_orig | ngrey | npseudo | nfire | nbluered | nred
--------+-------+---------+-------+----------+------
1 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3
Examples: Compare different color map looks using ST_AsPNG
SELECT ST_AsPNG(rast) As orig_png, ST_AsPNG(ST_ColorMap(rast,1,'greyscale')) As grey_png, ST_AsPNG(ST_ColorMap(rast,1, 'pseudocolor')) As pseudo_png, ST_AsPNG(ST_ColorMap(rast,1, 'nfire')) As fire_png, ST_AsPNG(ST_ColorMap(rast,1, 'bluered')) As bluered_png, ST_AsPNG(ST_ColorMap(rast,1, ' 100% 255 0 0 80% 160 0 0 50% 130 0 0 30% 30 0 0 20% 60 0 0 0% 0 0 0 nv 255 255 255 ')) As red_png FROM funky_shapes;
|
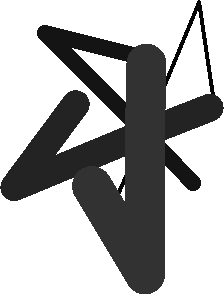
orig_png
|
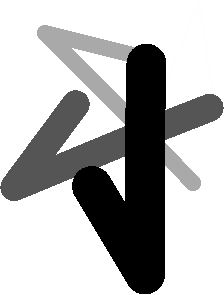
grey_png
|
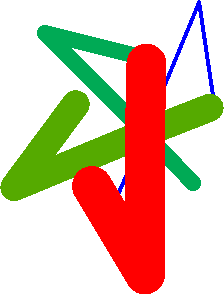
pseudo_png
|
|

fire_png
|
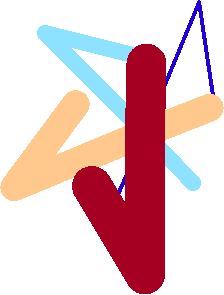
bluered_png
|
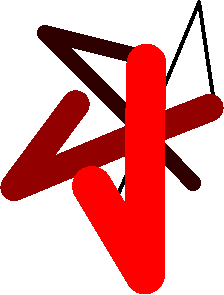
red_png
|
See Also
ST_AsPNG , ST_AsRaster ST_MapAlgebra , ST_NumBands , ST_Reclass , ST_SetBandNoDataValue , ST_Union