ST_Contains
Name
ST_Contains — Tests if no points of B lie in the exterior of A, and A and B have at least one interior point in common.
Synopsis
boolean
ST_Contains
(
geometry
geomA
, geometry
geomB
)
;
Description
Returns TRUE if geometry B is completely inside geometry A. A contains B if and only if no points of B lie in the exterior of A, and at least one point of the interior of B lies in the interior of A.
A subtlety of the definition is that a geometry does not contain things in its boundary. Thus polygons and lines do not contain lines and points lying in their boundary. For further details see Subtleties of OGC Covers, Contains, Within . (The ST_Covers predicate provides a more inclusive relationship.) However, a geometry does contain itself. (In contrast, in the ST_ContainsProperly predicate a geometry does not properly contain itself.)
ST_Contains is the inverse of
ST_Within
.
So,
ST_Contains(A,B) = ST_Within(B,A)
.
![[Note]](images/note.png)
|
|
|
This function automatically includes a bounding box comparison
that makes use of any spatial indexes that are available on the geometries.
To avoid index use, use the function
|
Performed by the GEOS module
Enhanced: 2.3.0 Enhancement to PIP short-circuit extended to support MultiPoints with few points. Prior versions only supported point in polygon.
![[Important]](images/important.png)
|
|
|
Enhanced: 3.0.0 enabled support for
|
![[Important]](images/important.png)
|
|
|
Do not use this function with invalid geometries. You will get unexpected results. |
NOTE: this is the "allowable" version that returns a boolean, not an integer.
 This method implements the
OGC Simple Features
Implementation Specification for SQL 1.1.
s2.1.1.2 // s2.1.13.3
- same as within(geometry B, geometry A)
This method implements the
OGC Simple Features
Implementation Specification for SQL 1.1.
s2.1.1.2 // s2.1.13.3
- same as within(geometry B, geometry A)
 This method implements the SQL/MM specification. SQL-MM 3: 5.1.31
This method implements the SQL/MM specification. SQL-MM 3: 5.1.31
Examples
ST_Contains
returns
TRUE
in the following situations:
|
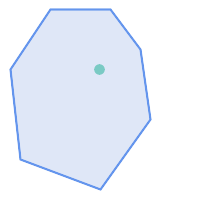
|

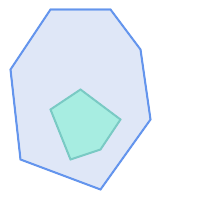
|
|
The
ST_Contains
predicate returns
FALSE
in the following situations:
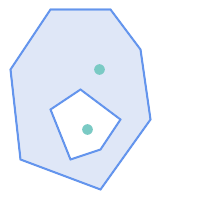
|
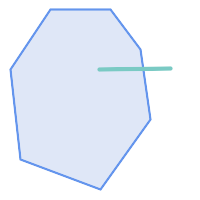
|
-- A circle within a circle
SELECT ST_Contains(smallc, bigc) As smallcontainsbig,
ST_Contains(bigc,smallc) As bigcontainssmall,
ST_Contains(bigc, ST_Union(smallc, bigc)) as bigcontainsunion,
ST_Equals(bigc, ST_Union(smallc, bigc)) as bigisunion,
ST_Covers(bigc, ST_ExteriorRing(bigc)) As bigcoversexterior,
ST_Contains(bigc, ST_ExteriorRing(bigc)) As bigcontainsexterior
FROM (SELECT ST_Buffer(ST_GeomFromText('POINT(1 2)'), 10) As smallc,
ST_Buffer(ST_GeomFromText('POINT(1 2)'), 20) As bigc) As foo;
-- Result
smallcontainsbig | bigcontainssmall | bigcontainsunion | bigisunion | bigcoversexterior | bigcontainsexterior
------------------+------------------+------------------+------------+-------------------+---------------------
f | t | t | t | t | f
-- Example demonstrating difference between contains and contains properly
SELECT ST_GeometryType(geomA) As geomtype, ST_Contains(geomA,geomA) AS acontainsa, ST_ContainsProperly(geomA, geomA) AS acontainspropa,
ST_Contains(geomA, ST_Boundary(geomA)) As acontainsba, ST_ContainsProperly(geomA, ST_Boundary(geomA)) As acontainspropba
FROM (VALUES ( ST_Buffer(ST_Point(1,1), 5,1) ),
( ST_MakeLine(ST_Point(1,1), ST_Point(-1,-1) ) ),
( ST_Point(1,1) )
) As foo(geomA);
geomtype | acontainsa | acontainspropa | acontainsba | acontainspropba
--------------+------------+----------------+-------------+-----------------
ST_Polygon | t | f | f | f
ST_LineString | t | f | f | f
ST_Point | t | t | f | f