ST_Contains
Name
ST_Contains — Tests if every point of B lies in A, and their interiors have a point in common
Synopsis
boolean
ST_Contains
(
geometry
geomA
, geometry
geomB
)
;
Description
Returns TRUE if geometry A contains geometry B. A contains B if and only if all points of B lie inside (i.e. in the interior or boundary of) A (or equivalently, no points of B lie in the exterior of A), and the interiors of A and B have at least one point in common.
In mathematical terms: ST_Contains(A, B) ⇔ (A ⋂ B = B) ∧ (Int(A) ⋂ Int(B) ≠ ∅)
The contains relationship is reflexive: every geometry contains itself.
(In contrast, in the
ST_ContainsProperly
predicate a geometry does
not
properly contain itself.)
The relationship is antisymmetric: if
ST_Contains(A,B) = true
and
ST_Contains(B,A) = true
, then
the two geometries must be topologically equal (
ST_Equals(A,B) = true
).
ST_Contains is the converse of
ST_Within
.
So,
ST_Contains(A,B) = ST_Within(B,A)
.
![[Note]](./images/note.png)
|
|
|
Because the interiors must have a common point, a subtlety of the definition is that polygons and lines do not contain lines and points lying fully in their boundary. For further details see Subtleties of OGC Covers, Contains, Within . The ST_Covers predicate provides a more inclusive relationship. |
![[Note]](./images/note.png)
|
|
|
This function automatically includes a bounding box comparison
that makes use of any spatial indexes that are available on the geometries.
To avoid index use, use the function
|
Performed by the GEOS module
Enhanced: 2.3.0 Enhancement to PIP short-circuit extended to support MultiPoints with few points. Prior versions only supported point in polygon.
![[Important]](./images/important.png)
|
|
|
Enhanced: 3.0.0 enabled support for
|
![[Important]](./images/important.png)
|
|
|
Do not use this function with invalid geometries. You will get unexpected results. |
NOTE: this is the "allowable" version that returns a boolean, not an integer.
 This method implements the
OGC Simple Features
Implementation Specification for SQL 1.1.
s2.1.1.2 // s2.1.13.3
- same as within(geometry B, geometry A)
This method implements the
OGC Simple Features
Implementation Specification for SQL 1.1.
s2.1.1.2 // s2.1.13.3
- same as within(geometry B, geometry A)
 This method implements the SQL/MM specification.
SQL-MM 3: 5.1.31
This method implements the SQL/MM specification.
SQL-MM 3: 5.1.31
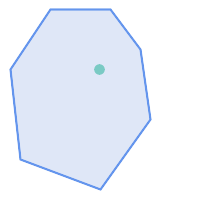
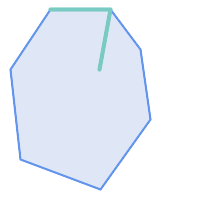
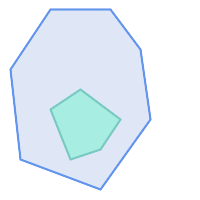
Examples
ST_Contains
returns
TRUE
in the following situations:
|
|
|
|
ST_Contains
returns
FALSE
in the following situations:
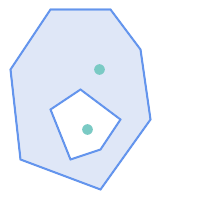
|
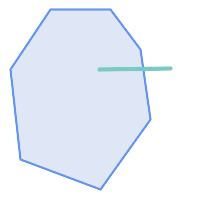
|
Due to the interior intersection condition
ST_Contains
returns
FALSE
in the following situations
(whereas
ST_Covers
returns
TRUE
):
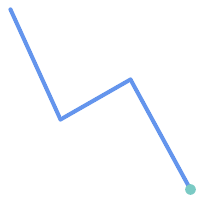
|
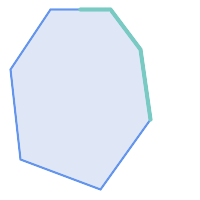
|
-- A circle within a circle
SELECT ST_Contains(smallc, bigc) As smallcontainsbig,
ST_Contains(bigc,smallc) As bigcontainssmall,
ST_Contains(bigc, ST_Union(smallc, bigc)) as bigcontainsunion,
ST_Equals(bigc, ST_Union(smallc, bigc)) as bigisunion,
ST_Covers(bigc, ST_ExteriorRing(bigc)) As bigcoversexterior,
ST_Contains(bigc, ST_ExteriorRing(bigc)) As bigcontainsexterior
FROM (SELECT ST_Buffer(ST_GeomFromText('POINT(1 2)'), 10) As smallc,
ST_Buffer(ST_GeomFromText('POINT(1 2)'), 20) As bigc) As foo;
-- Result
smallcontainsbig | bigcontainssmall | bigcontainsunion | bigisunion | bigcoversexterior | bigcontainsexterior
------------------+------------------+------------------+------------+-------------------+---------------------
f | t | t | t | t | f
-- Example demonstrating difference between contains and contains properly
SELECT ST_GeometryType(geomA) As geomtype, ST_Contains(geomA,geomA) AS acontainsa, ST_ContainsProperly(geomA, geomA) AS acontainspropa,
ST_Contains(geomA, ST_Boundary(geomA)) As acontainsba, ST_ContainsProperly(geomA, ST_Boundary(geomA)) As acontainspropba
FROM (VALUES ( ST_Buffer(ST_Point(1,1), 5,1) ),
( ST_MakeLine(ST_Point(1,1), ST_Point(-1,-1) ) ),
( ST_Point(1,1) )
) As foo(geomA);
geomtype | acontainsa | acontainspropa | acontainsba | acontainspropba
--------------+------------+----------------+-------------+-----------------
ST_Polygon | t | f | f | f
ST_LineString | t | f | f | f
ST_Point | t | t | f | f
See Also
ST_Boundary , ST_ContainsProperly , ST_Covers , ST_CoveredBy , ST_Equals , ST_Within