High Availability
One of the great things about PostgreSQL is its reliability: it is very stable and typically “just works.” However, there are certain things that can happen in the environment that PostgreSQL is deployed in that can affect its uptime, including:
- The database storage disk fails or some other hardware failure occurs
- The network on which the database resides becomes unreachable
- The host operating system becomes unstable and crashes
- A key database file becomes corrupted
- A data center is lost
There may also be downtime events that are due to the normal case of operations, such as performing a minor upgrade, security patching of operating system, hardware upgrade, or other maintenance.
Fortunately, the Crunchy PostgreSQL Operator is prepared for this.
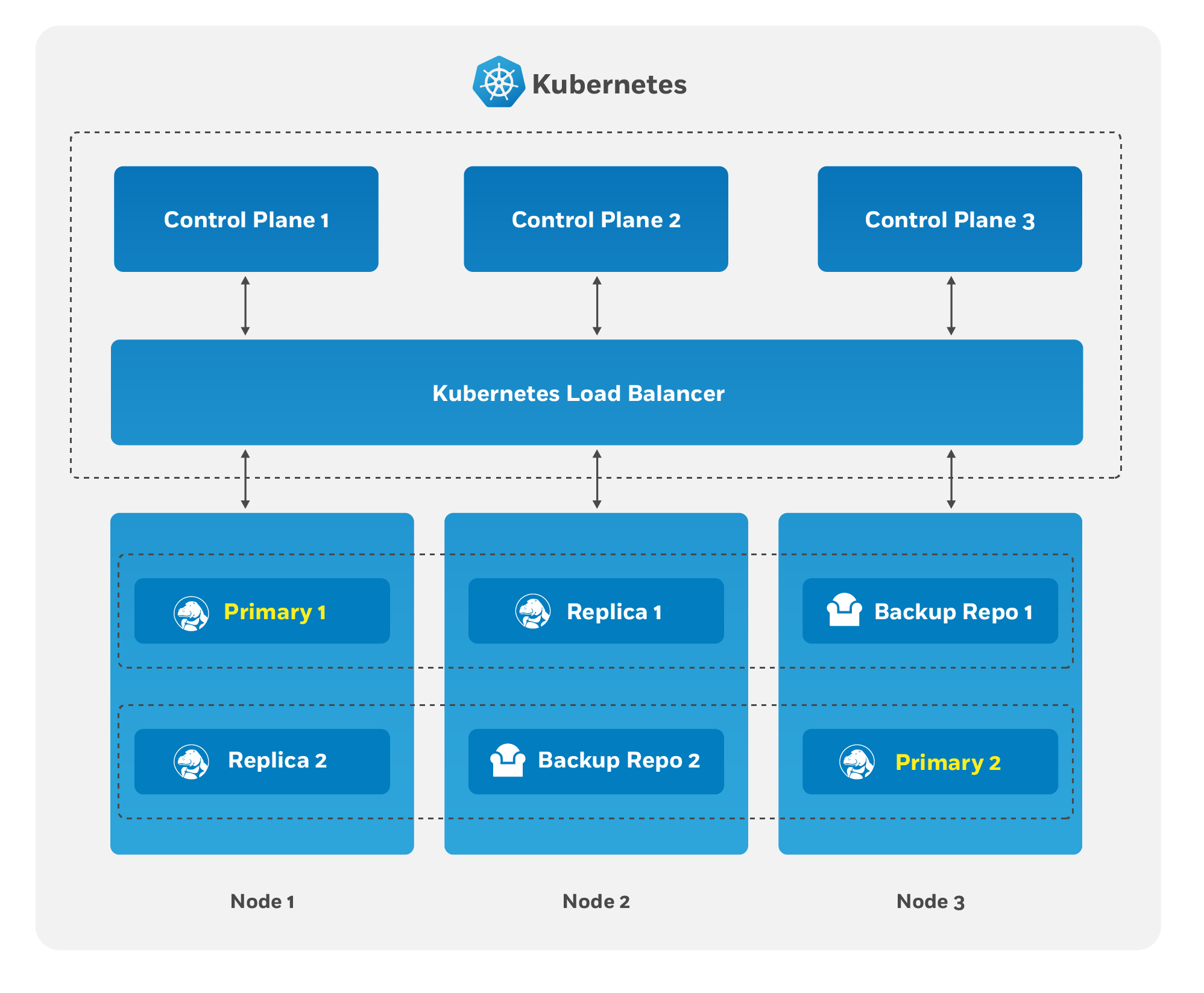
The Crunchy PostgreSQL Operator supports a distributed-consensus based high-availability (HA) system that keeps its managed PostgreSQL clusters up and running, even if the PostgreSQL Operator disappears. Additionally, it leverages Kubernetes specific features such as Pod Anti-Affinity to limit the surface area that could lead to a PostgreSQL cluster becoming unavailable. The PostgreSQL Operator also supports automatic healing of failed primaries and leverages the efficient pgBackRest “delta restore” method, which eliminates the need to fully reprovision a failed cluster!
This tutorial will cover the “howtos” of high availbility. For more information on the topic, please review the detailed high availability architecture section.
Create a HA PostgreSQL Cluster
High availability is enabled in the PostgreSQL Operator by default so long as you have more than one replica. To create a high availability PostgreSQL cluster, you can execute the following command:
pgo create cluster hippo --replica-count=1
Scale a PostgreSQL Cluster
You can scale an existing PostgreSQL cluster to add HA to it by using the pgo scale command:
pgo scale hippo
Scale Down a PostgreSQL Cluster
To scale down a PostgreSQL cluster, you will have to provide a target of which instance you want to scale down. You can do this with the pgo scaledown command:
pgo scaledown hippo --query
which will yield something similar to:
Cluster: hippo
REPLICA STATUS NODE REPLICATION LAG PENDING RESTART
hippo-ojnd running node01 0 MB false
Once you have determined which instance you want to scale down, you can run the following command:
pgo scaledown hippo --target=hippo-ojnd
Manual Failover
Each PostgreSQL cluster will manage its own availability. If you wish to manually fail over, you will need to use the pgo failover command. First, determine which instance you want to fail over to:
pgo failover hippo --query
which will yield something similar to:
Cluster: hippo
REPLICA STATUS NODE REPLICATION LAG PENDING RESTART
hippo-ojnd running node01 0 MB false
Once you have determine your failover target, you can run the following command:
pgo failover hippo --target==hippo-ojnd
Synchronous Replication
If you have a write sensitive workload and wish to use synchronous replication, you can create your PostgreSQL cluster with synchronous replication turned on:
pgo create cluster hippo --sync-replication
Please understand the tradeoffs of synchronous replication before using it.
Pod Anti-Affinity and Node Affinity
To leran how to use pod anti-affinity and node affinity, please refer to the high availability architecture documentation
Next Steps
Backups, restores, point-in-time-recoveries: disaster recovery is a big topic! We’ll learn about you can perform disaster recovery and more in the PostgreSQL Operator.