pgr_dijkstra - pgRouting Manual (3.8)
pgr_dijkstra
pgr_dijkstra
- Shortest path using Dijkstra algorithm.
Availability
-
Version 3.5.0
-
Standardizing output columns to
(seq, path_seq, start_vid, end_vid, node, edge, cost, agg_cost)-
pgr_dijkstra(One to One) added
start_vidandend_vidcolumns. -
pgr_dijkstra(One to Many) added
end_vidcolumn. -
pgr_dijkstra(Many to One) added
start_vidcolumn.
-
-
-
Version 3.1.0
-
New proposed signature:
-
pgr_dijkstra(Combinations)
-
-
-
Version 3.0.0
-
Function promoted to official.
-
-
Version 2.2.0
-
New proposed signatures:
-
pgr_dijkstra(One to Many)
-
pgr_dijkstra(Many to One)
-
pgr_dijkstra(Many to Many)
-
-
-
Version 2.1.0
-
Signature change on pgr_dijkstra(One to One)
-
-
Version 2.0.0
-
Official function.
-
Description
Dijkstra’s algorithm, conceived by Dutch computer scientist Edsger Dijkstra in 1956. It is a graph search algorithm that solves the shortest path problem for a graph with non-negative edge path costs, producing a shortest path from a starting vertex to an ending vertex. This implementation can be used with a directed graph and an undirected graph.
-
Process is done only on edges with positive costs.
-
A negative value on a cost column is interpreted as the edge does not exist.
-
-
Values are returned when there is a path.
-
When there is no path:
-
When the starting vertex and ending vertex are the same.
-
The aggregate cost of the non included values \((v, v)\) is \(0\)
-
-
When the starting vertex and ending vertex are the different and there is no path:
-
The aggregate cost the non included values \((u, v)\) is \(\infty\)
-
-
-
For optimization purposes, any duplicated value in the starting vertices or on the ending vertices are ignored.
-
Running time: \(O( start\ vids * (V \log V + E))\)
Signatures
Summary
directed
])
directed
])
directed
])
directed
])
(seq,
path_seq,
start_vid,
end_vid,
node,
edge,
cost,
agg_cost)
Warning
Breaking change on 3.5.0
Read the Migration guide about how to migrate from the old result columns to the new result columns.
One to One
directed
])
(seq,
path_seq,
start_vid,
end_vid,
node,
edge,
cost,
agg_cost)
- Example :
-
From vertex \(6\) to vertex \(10\) on a directed graph
SELECT * FROM pgr_Dijkstra(
'select id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost from edges',
6, 10, true);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 10 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 10 7 8 1 1
3 3 6 10 11 9 1 2
4 4 6 10 16 16 1 3
5 5 6 10 15 3 1 4
6 6 6 10 10 -1 0 5
(6 rows)
One to Many
directed
])
(seq,
path_seq,
start_vid,
end_vid,
node,
edge,
cost,
agg_cost)
- Example :
-
From vertex \(6\) to vertices \(\{10, 17\}\) on a directed
SELECT * FROM pgr_Dijkstra(
'select id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost from edges',
6, ARRAY[10, 17]);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 10 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 10 7 8 1 1
3 3 6 10 11 9 1 2
4 4 6 10 16 16 1 3
5 5 6 10 15 3 1 4
6 6 6 10 10 -1 0 5
7 1 6 17 6 4 1 0
8 2 6 17 7 8 1 1
9 3 6 17 11 9 1 2
10 4 6 17 16 15 1 3
11 5 6 17 17 -1 0 4
(11 rows)
Many to One
directed
])
(seq,
path_seq,
start_vid,
end_vid,
node,
edge,
cost,
agg_cost)
- Example :
-
From vertices \(\{6, 1\}\) to vertex \(17\) on a directed graph
SELECT * FROM pgr_Dijkstra(
'select id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost from edges',
ARRAY[6, 1], 17);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 1 17 1 6 1 0
2 2 1 17 3 7 1 1
3 3 1 17 7 8 1 2
4 4 1 17 11 11 1 3
5 5 1 17 12 13 1 4
6 6 1 17 17 -1 0 5
7 1 6 17 6 4 1 0
8 2 6 17 7 8 1 1
9 3 6 17 11 11 1 2
10 4 6 17 12 13 1 3
11 5 6 17 17 -1 0 4
(11 rows)
Many to Many
directed
])
(seq,
path_seq,
start_vid,
end_vid,
node,
edge,
cost,
agg_cost)
- Example :
-
From vertices \(\{6, 1\}\) to vertices \(\{10, 17\}\) on an undirected graph
SELECT * FROM pgr_Dijkstra(
'select id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost from edges',
ARRAY[6, 1], ARRAY[10, 17],
directed => false);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 1 10 1 6 1 0
2 2 1 10 3 7 1 1
3 3 1 10 7 4 1 2
4 4 1 10 6 2 1 3
5 5 1 10 10 -1 0 4
6 1 1 17 1 6 1 0
7 2 1 17 3 7 1 1
8 3 1 17 7 8 1 2
9 4 1 17 11 9 1 3
10 5 1 17 16 15 1 4
11 6 1 17 17 -1 0 5
12 1 6 10 6 2 1 0
13 2 6 10 10 -1 0 1
14 1 6 17 6 4 1 0
15 2 6 17 7 8 1 1
16 3 6 17 11 11 1 2
17 4 6 17 12 13 1 3
18 5 6 17 17 -1 0 4
(18 rows)
Combinations
(seq,
path_seq,
start_vid,
end_vid,
node,
edge,
cost,
agg_cost)
- Example :
-
Using a combinations table on an undirected graph
The combinations table:
SELECT source, target FROM combinations;
source target
--------+--------
5 6
5 10
6 5
6 15
6 14
(5 rows)
The query:
SELECT * FROM pgr_Dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edges',
'SELECT source, target FROM combinations',
false);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 5 6 5 1 1 0
2 2 5 6 6 -1 0 1
3 1 5 10 5 1 1 0
4 2 5 10 6 2 1 1
5 3 5 10 10 -1 0 2
6 1 6 5 6 1 1 0
7 2 6 5 5 -1 0 1
8 1 6 15 6 2 1 0
9 2 6 15 10 3 1 1
10 3 6 15 15 -1 0 2
(10 rows)
Parameters
|
Column |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Edges SQL as described below |
|
|
|
Combinations SQL as described below |
|
|
start vid |
|
Identifier of the starting vertex of the path. |
|
start vids |
|
Array of identifiers of starting vertices. |
|
end vid |
|
Identifier of the ending vertex of the path. |
|
end vids |
|
Array of identifiers of ending vertices. |
Optional parameters
|
Column |
Type |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Inner Queries
Edges SQL
|
Column |
Type |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
ANY-INTEGER |
Identifier of the edge. |
|
|
|
ANY-INTEGER |
Identifier of the first end point vertex of the edge. |
|
|
|
ANY-INTEGER |
Identifier of the second end point vertex of the edge. |
|
|
|
ANY-NUMERICAL |
Weight of the edge (
|
|
|
|
ANY-NUMERICAL |
-1 |
Weight of the edge (
|
Where:
- ANY-INTEGER :
-
SMALLINT,INTEGER,BIGINT - ANY-NUMERICAL :
-
SMALLINT,INTEGER,BIGINT,REAL,FLOAT
Combinations SQL
|
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
ANY-INTEGER |
Identifier of the departure vertex. |
|
|
ANY-INTEGER |
Identifier of the arrival vertex. |
Where:
- ANY-INTEGER :
-
SMALLINT,INTEGER,BIGINT
Result columns
Returns set of
(seq,
path_seq
[,
start_vid]
[,
end_vid],
node,
edge,
cost,
agg_cost)
|
Column |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Sequential value starting from 1 . |
|
|
|
Relative position in the path. Has value 1 for the beginning of a path. |
|
|
|
Identifier of the starting vertex. Returned when multiple starting vetrices are in the query. |
|
|
|
Identifier of the ending vertex. Returned when multiple ending vertices are in the query. |
|
|
|
Identifier of the node in the path from
|
|
|
|
Identifier of the edge used to go from
|
|
|
|
Cost to traverse from
|
|
|
|
Aggregate cost from
|
Additional Examples
- Example :
-
Demonstration of repeated values are ignored, and result is sorted.
SELECT * FROM pgr_Dijkstra(
'select id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost from edges',
ARRAY[7, 10, 15, 10, 10, 15], ARRAY[10, 7, 10, 15]);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 7 10 7 8 1 0
2 2 7 10 11 9 1 1
3 3 7 10 16 16 1 2
4 4 7 10 15 3 1 3
5 5 7 10 10 -1 0 4
6 1 7 15 7 8 1 0
7 2 7 15 11 9 1 1
8 3 7 15 16 16 1 2
9 4 7 15 15 -1 0 3
10 1 10 7 10 5 1 0
11 2 10 7 11 8 1 1
12 3 10 7 7 -1 0 2
13 1 10 15 10 5 1 0
14 2 10 15 11 9 1 1
15 3 10 15 16 16 1 2
16 4 10 15 15 -1 0 3
17 1 15 7 15 16 1 0
18 2 15 7 16 9 1 1
19 3 15 7 11 8 1 2
20 4 15 7 7 -1 0 3
21 1 15 10 15 3 1 0
22 2 15 10 10 -1 0 1
(22 rows)
- Example 2 :
-
Making start_vids the same as end_vids
SELECT * FROM pgr_Dijkstra(
'select id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost from edges',
ARRAY[7, 10, 15], ARRAY[7, 10, 15]);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 7 10 7 8 1 0
2 2 7 10 11 9 1 1
3 3 7 10 16 16 1 2
4 4 7 10 15 3 1 3
5 5 7 10 10 -1 0 4
6 1 7 15 7 8 1 0
7 2 7 15 11 9 1 1
8 3 7 15 16 16 1 2
9 4 7 15 15 -1 0 3
10 1 10 7 10 5 1 0
11 2 10 7 11 8 1 1
12 3 10 7 7 -1 0 2
13 1 10 15 10 5 1 0
14 2 10 15 11 9 1 1
15 3 10 15 16 16 1 2
16 4 10 15 15 -1 0 3
17 1 15 7 15 16 1 0
18 2 15 7 16 9 1 1
19 3 15 7 11 8 1 2
20 4 15 7 7 -1 0 3
21 1 15 10 15 3 1 0
22 2 15 10 10 -1 0 1
(22 rows)
- Example :
-
Manually assigned vertex combinations.
SELECT * FROM pgr_Dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edges',
'SELECT * FROM (VALUES (6, 10), (6, 7), (12, 10)) AS combinations (source, target)');
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 7 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 7 7 -1 0 1
3 1 6 10 6 4 1 0
4 2 6 10 7 8 1 1
5 3 6 10 11 9 1 2
6 4 6 10 16 16 1 3
7 5 6 10 15 3 1 4
8 6 6 10 10 -1 0 5
9 1 12 10 12 13 1 0
10 2 12 10 17 15 1 1
11 3 12 10 16 16 1 2
12 4 12 10 15 3 1 3
13 5 12 10 10 -1 0 4
(13 rows)
The examples of this section are based on the Sample Data network.
For
directed
graphs with
cost
and
reverse_cost
columns
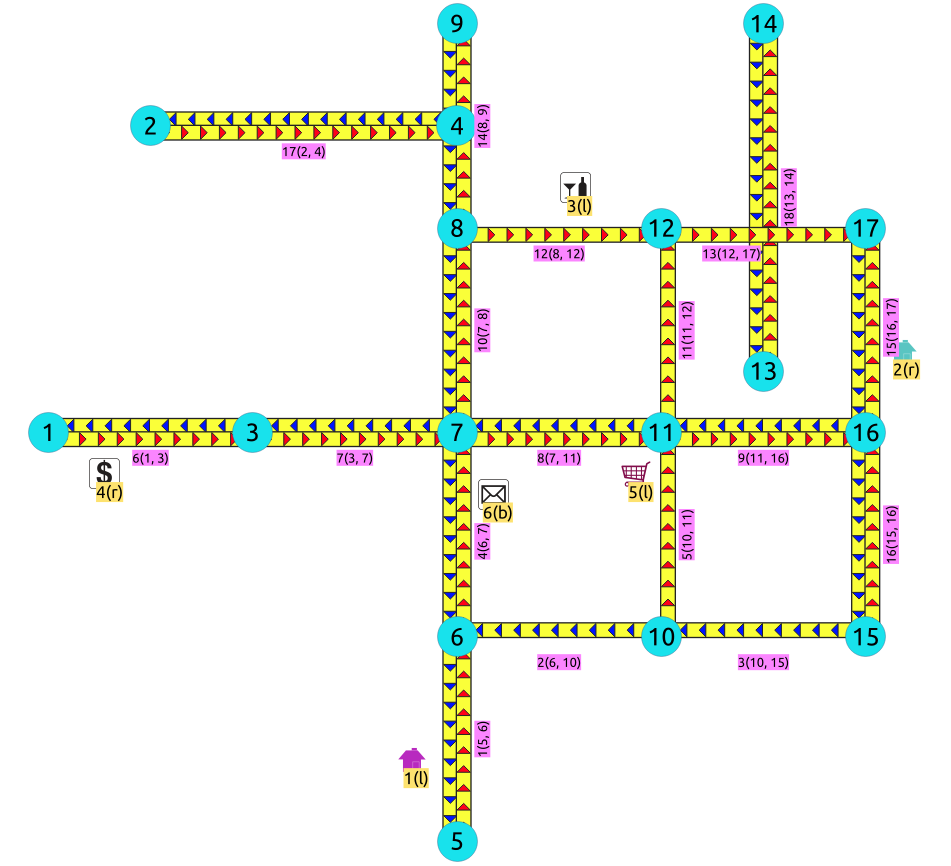
1) Path from \(6\) to \(10\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edges',
6, 10
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 10 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 10 7 8 1 1
3 3 6 10 11 9 1 2
4 4 6 10 16 16 1 3
5 5 6 10 15 3 1 4
6 6 6 10 10 -1 0 5
(6 rows)
2) Path from \(6\) to \(7\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edges',
6, 7
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 7 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 7 7 -1 0 1
(2 rows)
3) Path from \(12\) to \(10\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edges',
12, 10
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 12 10 12 13 1 0
2 2 12 10 17 15 1 1
3 3 12 10 16 16 1 2
4 4 12 10 15 3 1 3
5 5 12 10 10 -1 0 4
(5 rows)
4) Path from \(12\) to \(7\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edges',
12, 7
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 12 7 12 13 1 0
2 2 12 7 17 15 1 1
3 3 12 7 16 9 1 2
4 4 12 7 11 8 1 3
5 5 12 7 7 -1 0 4
(5 rows)
5) Using One to Many to get the solution of examples 1 and 2
Paths \(\{6\}\rightarrow\{10, 7\}\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edges',
6, ARRAY[10, 7]
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 7 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 7 7 -1 0 1
3 1 6 10 6 4 1 0
4 2 6 10 7 8 1 1
5 3 6 10 11 9 1 2
6 4 6 10 16 16 1 3
7 5 6 10 15 3 1 4
8 6 6 10 10 -1 0 5
(8 rows)
6) Using Many to One to get the solution of examples 2 and 4
Paths \(\{6, 12\}\rightarrow\{7\}\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edges',
ARRAY[6, 12], 7
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 7 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 7 7 -1 0 1
3 1 12 7 12 13 1 0
4 2 12 7 17 15 1 1
5 3 12 7 16 9 1 2
6 4 12 7 11 8 1 3
7 5 12 7 7 -1 0 4
(7 rows)
7) Using Many to Many to get the solution of examples 1 to 4
Paths \(\{6, 12\}\rightarrow\{10, 7\}\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edges',
ARRAY[6, 12], ARRAY[10,7]
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 7 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 7 7 -1 0 1
3 1 6 10 6 4 1 0
4 2 6 10 7 8 1 1
5 3 6 10 11 9 1 2
6 4 6 10 16 16 1 3
7 5 6 10 15 3 1 4
8 6 6 10 10 -1 0 5
9 1 12 7 12 13 1 0
10 2 12 7 17 15 1 1
11 3 12 7 16 9 1 2
12 4 12 7 11 8 1 3
13 5 12 7 7 -1 0 4
14 1 12 10 12 13 1 0
15 2 12 10 17 15 1 1
16 3 12 10 16 16 1 2
17 4 12 10 15 3 1 3
18 5 12 10 10 -1 0 4
(18 rows)
8) Using Combinations to get the solution of examples 1 to 3
Paths \(\{6\}\rightarrow\{10, 7\}\cup\{12\}\rightarrow\{10\}\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edges',
'SELECT * FROM (VALUES (6, 10), (6, 7), (12, 10)) AS combinations (source, target)'
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 7 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 7 7 -1 0 1
3 1 6 10 6 4 1 0
4 2 6 10 7 8 1 1
5 3 6 10 11 9 1 2
6 4 6 10 16 16 1 3
7 5 6 10 15 3 1 4
8 6 6 10 10 -1 0 5
9 1 12 10 12 13 1 0
10 2 12 10 17 15 1 1
11 3 12 10 16 16 1 2
12 4 12 10 15 3 1 3
13 5 12 10 10 -1 0 4
(13 rows)
For
undirected
graphs with
cost
and
reverse_cost
columns
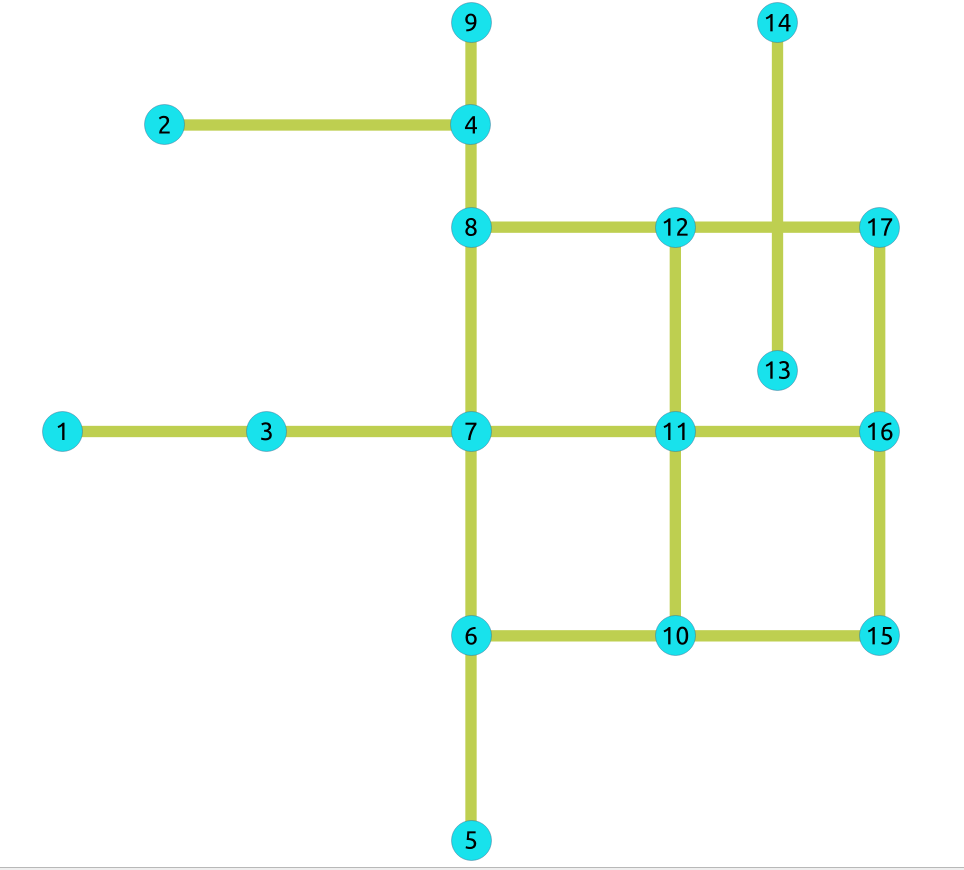
9) Path from \(6\) to \(10\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edges',
6, 10,
false
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 10 6 2 1 0
2 2 6 10 10 -1 0 1
(2 rows)
10) Path from \(6\) to \(7\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edges',
6, 7,
false
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 7 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 7 7 -1 0 1
(2 rows)
11) Path from \(12\) to \(10\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edges',
12, 10,
false
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 12 10 12 11 1 0
2 2 12 10 11 5 1 1
3 3 12 10 10 -1 0 2
(3 rows)
12) Path from \(12\) to \(7\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edges',
12, 7,
false
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 12 7 12 12 1 0
2 2 12 7 8 10 1 1
3 3 12 7 7 -1 0 2
(3 rows)
13) Using One to Many to get the solution of examples 9 and 10
Paths \(\{6\}\rightarrow\{10, 7\}\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edges',
6, ARRAY[10,7],
false
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 7 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 7 7 -1 0 1
3 1 6 10 6 2 1 0
4 2 6 10 10 -1 0 1
(4 rows)
14) Using Many to One to get the solution of examples 10 and 12
Paths \(\{6, 12\}\rightarrow\{7\}\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edges',
ARRAY[6,12], 7,
false
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 7 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 7 7 -1 0 1
3 1 12 7 12 12 1 0
4 2 12 7 8 10 1 1
5 3 12 7 7 -1 0 2
(5 rows)
15) Using Many to Many to get the solution of examples 9 to 12
Paths \(\{6, 12\}\rightarrow\{10, 7\}\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edges',
ARRAY[6, 12], ARRAY[10,7],
false
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 7 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 7 7 -1 0 1
3 1 6 10 6 2 1 0
4 2 6 10 10 -1 0 1
5 1 12 7 12 12 1 0
6 2 12 7 8 10 1 1
7 3 12 7 7 -1 0 2
8 1 12 10 12 11 1 0
9 2 12 10 11 5 1 1
10 3 12 10 10 -1 0 2
(10 rows)
16) Using Combinations to get the solution of examples 9 to 11
Paths \(\{6\}\rightarrow\{10, 7\}\cup\{12\}\rightarrow\{10\}\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edges',
'SELECT * FROM (VALUES (6, 10), (6, 7), (12, 10)) AS combinations (source, target)',
false
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 7 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 7 7 -1 0 1
3 1 6 10 6 2 1 0
4 2 6 10 10 -1 0 1
5 1 12 10 12 11 1 0
6 2 12 10 11 5 1 1
7 3 12 10 10 -1 0 2
(7 rows)
For
directed
graphs only with
cost
column
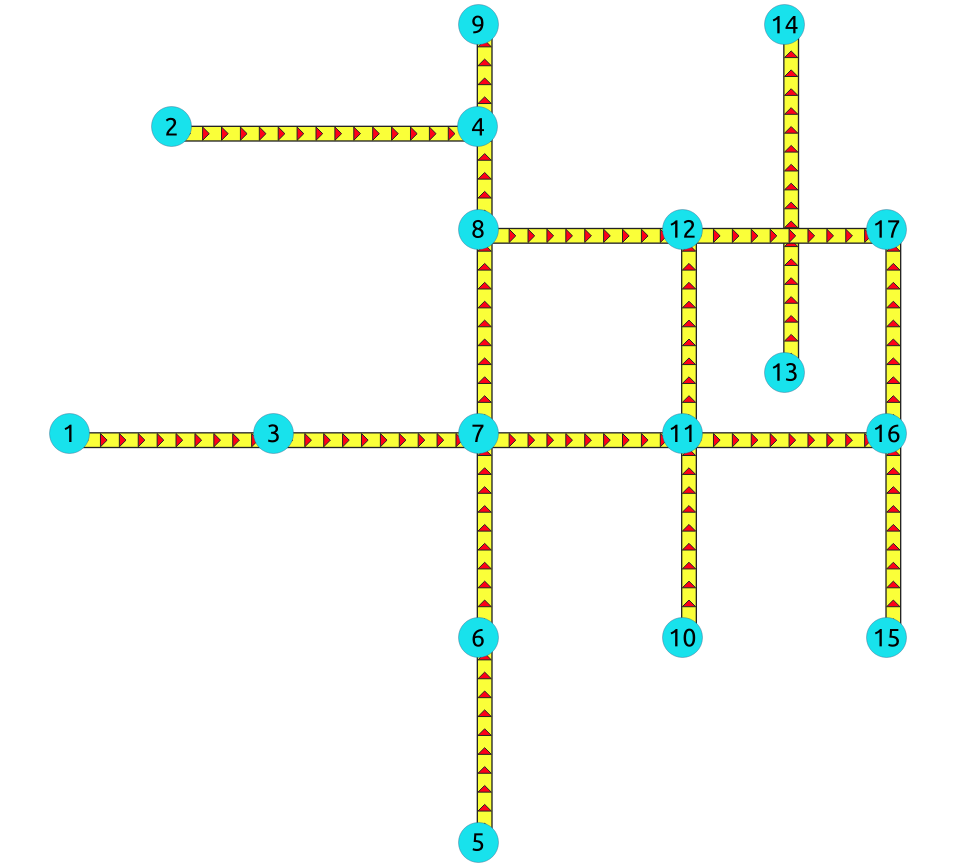
17) Path from \(6\) to \(10\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost FROM edges',
6, 10
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
(0 rows)
18) Path from \(6\) to \(7\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost FROM edges',
6, 7
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 7 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 7 7 -1 0 1
(2 rows)
19) Path from \(12\) to \(10\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost FROM edges',
12, 10
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
(0 rows)
20) Path from \(12\) to \(7\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost FROM edges',
12, 7
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
(0 rows)
21) Using One to Many to get the solution of examples 17 and 18
Paths \(\{6\}\rightarrow\{10, 7\}\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost FROM edges',
6, ARRAY[10,7]
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 7 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 7 7 -1 0 1
(2 rows)
22) Using Many to One to get the solution of examples 18 and 20
Paths \(\{6, 12\}\rightarrow\{7\}\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost FROM edges',
ARRAY[6,12], 7
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 7 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 7 7 -1 0 1
(2 rows)
23) Using Many to Many to get the solution of examples 17 to 20
Paths \(\{6, 12\}\rightarrow\{10, 7\}\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost FROM edges',
ARRAY[6, 12], ARRAY[10,7]
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 7 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 7 7 -1 0 1
(2 rows)
24) Using Combinations to get the solution of examples 17 to 19
Paths \(\{6\}\rightarrow\{10, 7\}\cup\{12\}\rightarrow\{10\}\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost FROM edges',
'SELECT * FROM (VALUES (6, 10), (6, 7), (12, 10)) AS combinations (source, target)'
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 7 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 7 7 -1 0 1
(2 rows)
For
undirected
graphs only with
cost
column
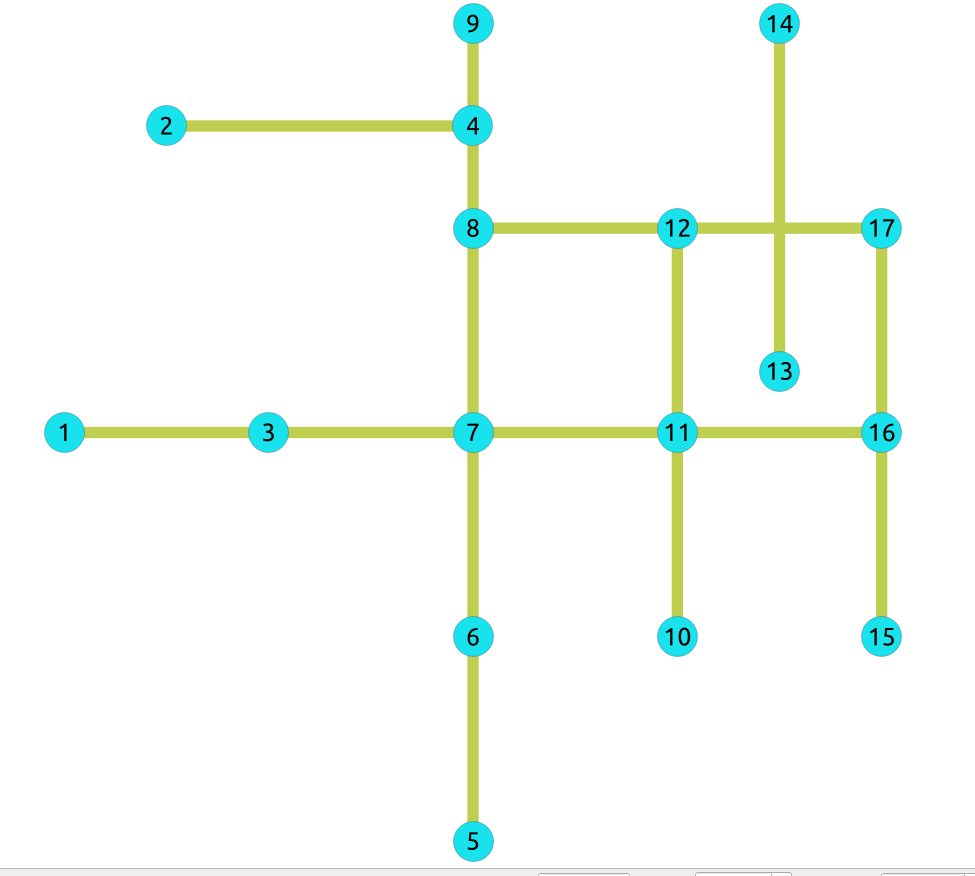
25) Path from \(6\) to \(10\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost FROM edges',
6, 10,
false
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 10 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 10 7 8 1 1
3 3 6 10 11 5 1 2
4 4 6 10 10 -1 0 3
(4 rows)
26) Path from \(6\) to \(7\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost FROM edges',
6, 7,
false
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 7 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 7 7 -1 0 1
(2 rows)
27) Path from \(12\) to \(10\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost FROM edges',
12, 10,
false
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 12 10 12 11 1 0
2 2 12 10 11 5 1 1
3 3 12 10 10 -1 0 2
(3 rows)
28) Path from \(12\) to \(7\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost FROM edges',
12, 7,
false
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 12 7 12 12 1 0
2 2 12 7 8 10 1 1
3 3 12 7 7 -1 0 2
(3 rows)
29) Using One to Many to get the solution of examples 25 and 26
Paths \(\{6\}\rightarrow\{10, 7\}\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost FROM edges',
6, ARRAY[10,7],
false
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 7 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 7 7 -1 0 1
3 1 6 10 6 4 1 0
4 2 6 10 7 8 1 1
5 3 6 10 11 5 1 2
6 4 6 10 10 -1 0 3
(6 rows)
30) Using Many to One to get the solution of examples 26 and 28
Paths \(\{6, 12\}\rightarrow\{7\}\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost FROM edges',
ARRAY[6,12], 7,
false
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 7 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 7 7 -1 0 1
3 1 12 7 12 12 1 0
4 2 12 7 8 10 1 1
5 3 12 7 7 -1 0 2
(5 rows)
31) Using Many to Many to get the solution of examples 25 to 28
Paths \(\{6, 12\}\rightarrow\{10, 7\}\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost FROM edges',
ARRAY[6, 12], ARRAY[10,7],
false
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 7 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 7 7 -1 0 1
3 1 6 10 6 4 1 0
4 2 6 10 7 8 1 1
5 3 6 10 11 5 1 2
6 4 6 10 10 -1 0 3
7 1 12 7 12 12 1 0
8 2 12 7 8 10 1 1
9 3 12 7 7 -1 0 2
10 1 12 10 12 11 1 0
11 2 12 10 11 5 1 1
12 3 12 10 10 -1 0 2
(12 rows)
32) Using Combinations to get the solution of examples 25 to 27
Paths \(\{6\}\rightarrow\{10, 7\}\cup\{12\}\rightarrow\{10\}\)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost FROM edges',
'SELECT * FROM (VALUES (6, 10), (6, 7), (12, 10)) AS combinations (source, target)',
false
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 7 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 7 7 -1 0 1
3 1 6 10 6 4 1 0
4 2 6 10 7 8 1 1
5 3 6 10 11 5 1 2
6 4 6 10 10 -1 0 3
7 1 12 10 12 11 1 0
8 2 12 10 11 5 1 1
9 3 12 10 10 -1 0 2
(9 rows)
Equvalences between signatures
The following examples find the path for \(\{6\}\rightarrow\{10\}\)
33) Using One to One
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edges',
6, 10
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 10 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 10 7 8 1 1
3 3 6 10 11 9 1 2
4 4 6 10 16 16 1 3
5 5 6 10 15 3 1 4
6 6 6 10 10 -1 0 5
(6 rows)
34) Using One to Many
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edges',
6, ARRAY[10]
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 10 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 10 7 8 1 1
3 3 6 10 11 9 1 2
4 4 6 10 16 16 1 3
5 5 6 10 15 3 1 4
6 6 6 10 10 -1 0 5
(6 rows)
35) Using Many to One
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edges',
ARRAY[6], 10
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 10 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 10 7 8 1 1
3 3 6 10 11 9 1 2
4 4 6 10 16 16 1 3
5 5 6 10 15 3 1 4
6 6 6 10 10 -1 0 5
(6 rows)
36) Using Many to Many
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edges',
ARRAY[6], ARRAY[10]
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 10 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 10 7 8 1 1
3 3 6 10 11 9 1 2
4 4 6 10 16 16 1 3
5 5 6 10 15 3 1 4
6 6 6 10 10 -1 0 5
(6 rows)
37) Using Combinations
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edges',
'SELECT * FROM (VALUES(6, 10)) AS combinations (source, target)'
);
seq path_seq start_vid end_vid node edge cost agg_cost
-----+----------+-----------+---------+------+------+------+----------
1 1 6 10 6 4 1 0
2 2 6 10 7 8 1 1
3 3 6 10 11 9 1 2
4 4 6 10 16 16 1 3
5 5 6 10 15 3 1 4
6 6 6 10 10 -1 0 5
(6 rows)
See Also
Indices and tables
